Enabling Safe and Inclusive Use of AI in Southeast Asia

Founding Executive Director, Tech for Good Institute

AI can play a crucial role in addressing the numerous and pressing needs of the region. Photo credit: iStock/Thicha Satapitanon.
Ensuring technology systems cater to the region's ethnic and cultural diversity is essential not only for AI but also for technology and tech-driven business models in general.
This article is published in collaboration with the Tech for Good Institute.
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have the potential to reshape our lives, work, education, and our perception of the world. Applications of AI can also accelerate progress toward the must-win challenges of our generation, from addressing climate change to achieving financial, health, and educational inclusion. Yet, this potential will not be realized if AI is not developed, deployed, and adopted safely and inclusively.
Southeast Asia’s ethnic and cultural diversity presents both challenges and opportunities for AI developers and deployers. Let us take Large Language Models—AI systems capable of understanding and generating human language by analyzing vast amounts of text—as an example. In our region, we encompass over 100 ethnic groups and speak over a thousand living languages and dialects. Many of today’s models are trained on content scraped from the web, of which over half is in English.
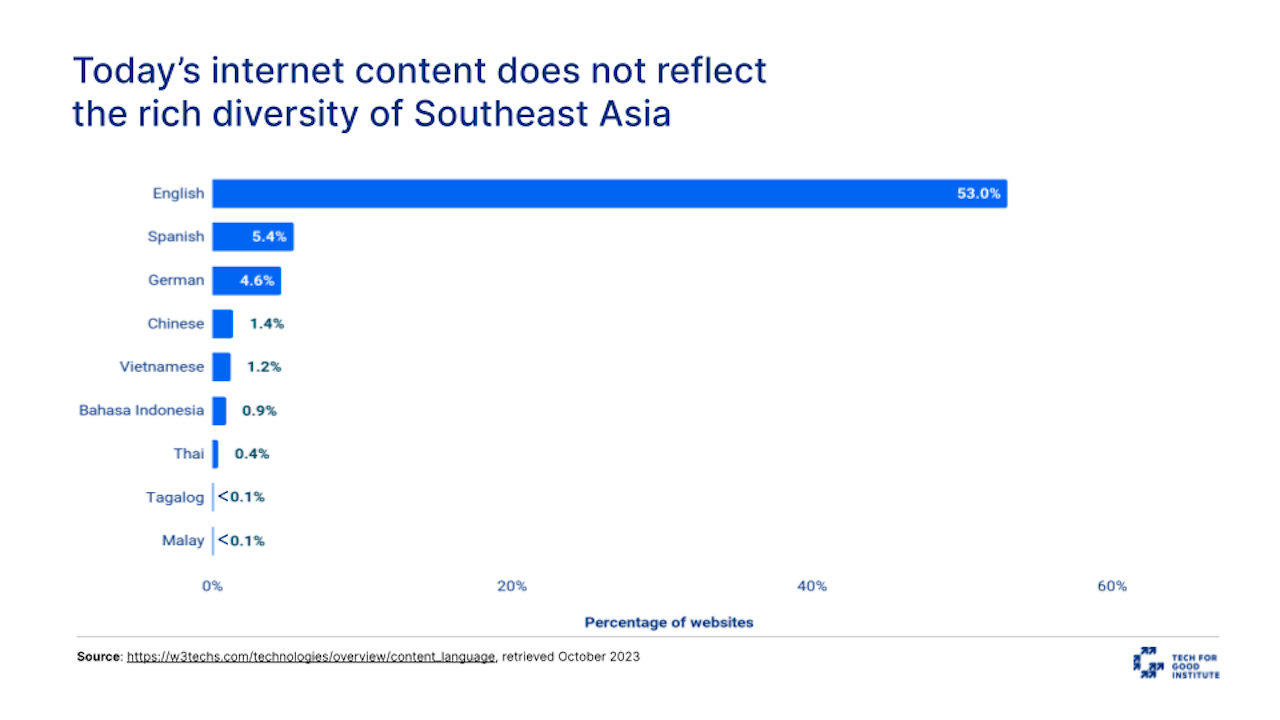
In fact, Mozilla’s Internet Health Report 2022 found that half of the datasets in the world are produced by just 12 elite institutions and tech companies in Germany; Hong Kong, China; and the United States. If left unchecked, there is a real risk that current real-world inequality and historical biases will be perpetuated in the digital space.
This presents an opportunity for companies in Southeast Asia. An example of a digital product built in Southeast Asia for Southeast Asia is GrabMaps. Across Southeast Asia, the definition of a "road" may be debatable. In addition to official roads seen on maps, locals know how to use footbridges and small alleyways, some just wide enough for a motorbike to drive through. In Indonesia, these "roads" are called jalan tikus, or rat alleys. Such alternative routes often do not show up on conventional maps that rely on satellite imagery or data collected from cameras on or in cars. Instead, Grab partnered with merchants, drivers, and delivery partners to aggregate data on a daily basis following the principles of community-based mapping. AI processing was used to cleanse and process this street view data into a digital map. These geospatial capabilities support Grab’s core business by helping its drivers and delivery riders reach destinations more quickly. As of 2023, GrabMaps has added more than 800,000 kilometers of missing "roads" to OpenStreetMap. Amazon Web Services now uses GrabMaps for its Amazon Location Service solution. Organizations spanning ecommerce, transportation, logistics, telecommunications, and government agencies are using this solution to improve their location-based services in Southeast Asia.
Addressing the region’s unique needs
To better capture Southeast Asia’s diversity, there is a need for relevant datasets and models that can address the region’s unique needs. AI can play a crucial role in addressing the numerous and pressing needs of the region. Earlier this year, the Tech for Good Institute conducted in-country roundtables across Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Viet Nam to understand how stakeholders in these tech ecosystems were envisioning the future trajectory of the digital economy. A common sentiment shared by over 130 participants from government agencies, digital economy companies, think tanks, and civil society organizations emphasized the importance of tech solutions that are fit-for-purpose. Impactful innovation requires first identifying the right problems to solve and then fostering the adoption of solutions. AI product companies embedded within the markets they serve are best positioned to achieve these goals. They can identify needs and gaps in the market and develop context-sensitive products and services. Continued investment in digital and AI capabilities should go beyond technical skills, such as machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and data analytics. It should also involve developing the skills and experience needed to bring AI products to market, integrating AI resources within existing organizations, aligning systems with society’s values and objectives, and coupling AI product capabilities with domain knowledge of specific industries, such as agritech, healthcare, or finance.
Another common theme from our stakeholder engagements was that the "Move Fast and Break Things" approach of the early internet era is no longer acceptable. We are witnessing a new paradigm that calls for accountability for the consequences and impact of technology products and services. Stakeholders highlighted the knowledge and data asymmetries between industry, academia, and government, as well as among different countries. There is a strong appetite for multi-stakeholder processes and transparent knowledge sharing to bridge this gap. AI practitioners who are eager to contribute to building a thriving innovation ecosystem would do well to be part of this conversation.
Governance of AI requires new thinking, given the emergent nature of the technology, as well as the application of existing tech policy elements, such as data protection, cybersecurity, and intellectual property. Countries across the region are at different stages of developing regulations in these areas. For example, regarding personal data protection, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Singapore passed data protection laws over a decade ago. Singapore’s latest amendments to the enforcement of the Personal Data Protection Act took effect in October 2022, while Malaysia has announced its intention to update its act. The Philippines has released issuances to supplement its Data Privacy Act of 2012. Indonesia and Viet Nam, on the other hand, only passed their laws in the last 2 years, and initial implementation is still in progress.
A case for good governance
Despite the challenges, good governance of the evolving digital ecosystem is vital. This governance is not meant to constrain innovation but to facilitate the trusted adoption of technology. Drawing on the Tech for Good Institute’s research on trust in digital financial services, it is worth bearing in mind that one’s propensity to trust technology does not necessarily predict trust in services enabled by technology. Instead, one of the most consistent predictors of trust across Southeast Asia is the perception of the service provider’s integrity. This includes having a strong sense of social justice and sound principles that demonstrably guide the company’s behavior. Hence, it is not enough to merely espouse generally accepted guiding principles along the lines of fairness, ethics, accountability, and transparency, although this is an important starting point. What is critical is evidence that these principles are put into practice. Just as ASEAN’s Model Contractual Clauses for Cross-Border Data Flows help small businesses ensure compliant transfer of personal data, practical assistance on implementing AI principles can help businesses procure, implement, develop, and deploy responsible AI products and services. Singapore’s AI Verify, for example, is one such practical way to support developers in testing and learning. Australia’s National AI Centre recently worked with the independent nonprofit Gradient Institute to provide practical guidance, tools, and guidelines for businesses to mature their responsible AI practices.
Finally, the safe and inclusive use of AI in Southeast Asia will only be possible if we consider the rapid individual-level changes in the region. Out of the 460 million internet users in Southeast Asia, 100 million have come online in the past 3 years. Not only are Southeast Asia’s new users a mobile-first and often mobile-only digital population, but they are also "AI-native." AI-powered tools such as chatbots, recommendation engines, and machine translation are part of their basic experience in a "normal" digital world. Digital literacy, therefore, needs to include algorithmic literacy, enabling users to safely navigate this AI-powered environment, recognize AI-generated content, understand biases, use AI critically while maintaining decision-making autonomy, and practise responsible AI use.
Southeast Asia is a rapidly changing, diverse, and very exciting region. Tailoring technology and governance to this diversity is essential, not only for AI specifically, but also for technology and tech-enabled business models in general. We need collaborative efforts from regional bodies like ASEAN, national governments, industry, and communities to harness the potential of AI safely with an approach that is regionally oriented, culturally inclusive, and locally feasible all at the same time.
This article was first published by the Tech for Good Institute on 4 January 2024.

Ming Tan
Founding Executive Director, Tech for Good InstituteMing Tan is founding executive director of Tech for Good Institute, which was founded by Grab to leverage the promise of technology to advance inclusive, equitable and sustainable growth for Southeast Asia. She is concurrently a senior fellow at the Centre for Governance and Sustainability at the National University of Singapore.

Tech for Good Institute
The Tech for Good Institute is a nonprofit organization working to leverage the promise of technology and the digital economy for inclusive, equitable, and sustainable growth in Southeast Asia. The Institute is seed funded by Grab, a leading superapp in Southeast Asia.


